Publications
Group highlights
(For a full list see below or go to Google Scholar or go see Current Projects)
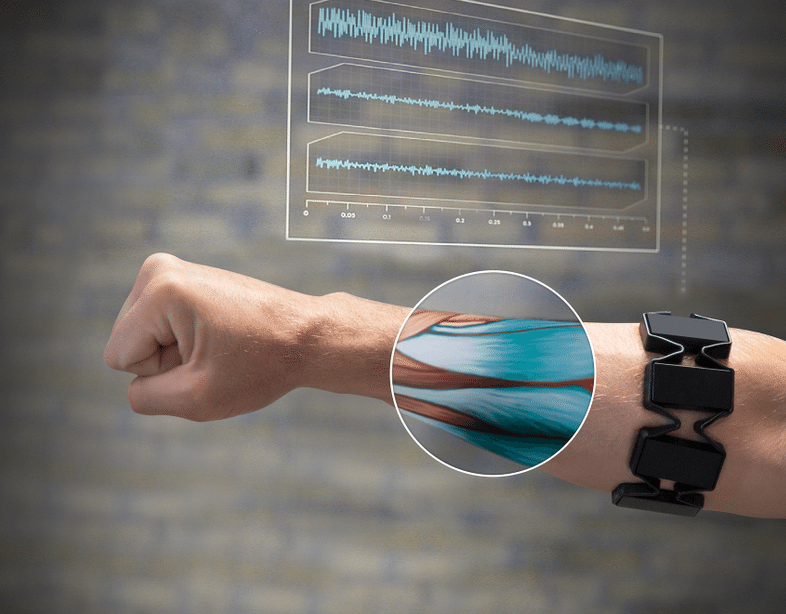
Myoelectric control is one of the leading brain-machine-interfaces in the field of robotic prosthetics. We present our research in real-time surface electromyography (sEMG) signal classification, where our simple and novel attention-based approach now leads the industry, universally beating more complex, state-of-the-art models. Our model achieved an accuracy of 87\%(class-balanced accuracy 69\%) using sEMG data and 91\%(balanced accuracy 74\%) using both sEMG and accelerometer (IMU) data on NinaPro DB5, as well as 73\% overall on NinaPro DB4, an improvement on both highly sophisticated deep learning and signal processing approaches. Notably, the representation of the data learned by the attention mechanism alone is powerful enough to yield an accuracy of 79\% on DB5. NinaPro DB5 is a standard benchmark for sEMG gesture recognition and consists of 53 unique gestures, including finger gestures, wrist gestures, and functional grasping gestures. Our proposed methodology’s model simplicity represents a compelling alternative to the convolutional neural network (CNN) approaches utilized in recent research.
D Josephs, C Drake, A Heroy, J Santerre -

In this paper, we present how electrical consumption can reveal insight into the novel COVID-19 pandemic spread. We analyze electrical power consumption provided by PPL Electric Utilities, Department of Labor’s unemployment claims, and the COVID-19 cases/deaths for the State of Pennsylvania to study the impact of the pandemic on the infrastructure. Using a SARIMA model as our benchmark and we analyzed the use of a SARIMAX model to forecast the power consumption in Pennsylvania 14 days ahead. Our work quantifies and illuminates the effect that the strict legislation passed to minimize the spread of COVID19 had a on power consumption. Most importantly, this study helps drive a greater understanding into the hidden cost of a global pandemic such as COVID-19.
J Au, J Saldaña Jr, B Spanswick, J Santerre
In this paper, we explore a representation methodology for the compression of DNA isolates. Using lossless string compression via tokenization of frequently repeated segments of DNA, we reduce the length of the isolates to be counted as k-mers for classification. With this new representation, we apply a previously established feature sampling method to dramatically reduce the feature space. In understanding the genetic diversity, we also look at conserving biological function across these spaces. Using a random forest model we were able to predict the resistance or susceptibility of bacteria with 85-90\% accuracy, with a 30-50\% reduction in overall isolate length, and an 80-90\% reduction in the feature space over baseline. Significant contributions were built upon previous analysis of similar data.
J Partee, R Hazell, A Solsi, J Santerre

In the current market, successful fitness tracking devices utilize heart rate and GPS to determine performance. These devices are useful, but don’t extensively classify stationary exercise. This paper proposes a modern approach for tuning and investigating optimal neural network types on stationary exercises using Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs). Using three IMUs located on the ankle, waist, and wrist, data is collected to map the body as it moves during the stationary physical activity. A novel five-stage deep learning tuning system was written and deployed to classify user movement as one of three classes air squats, jumping jacks, and kettlebell swings. It was determined that the ConvLSTM2D type is the most accurate and second fastest for training stationary exercise classification. Tracking of human movement extends to realms outside of fitness such as robotics, medical and military applications.
Andrew M Heroy, Zackary Gill, Samantha Sprague, J Santerre
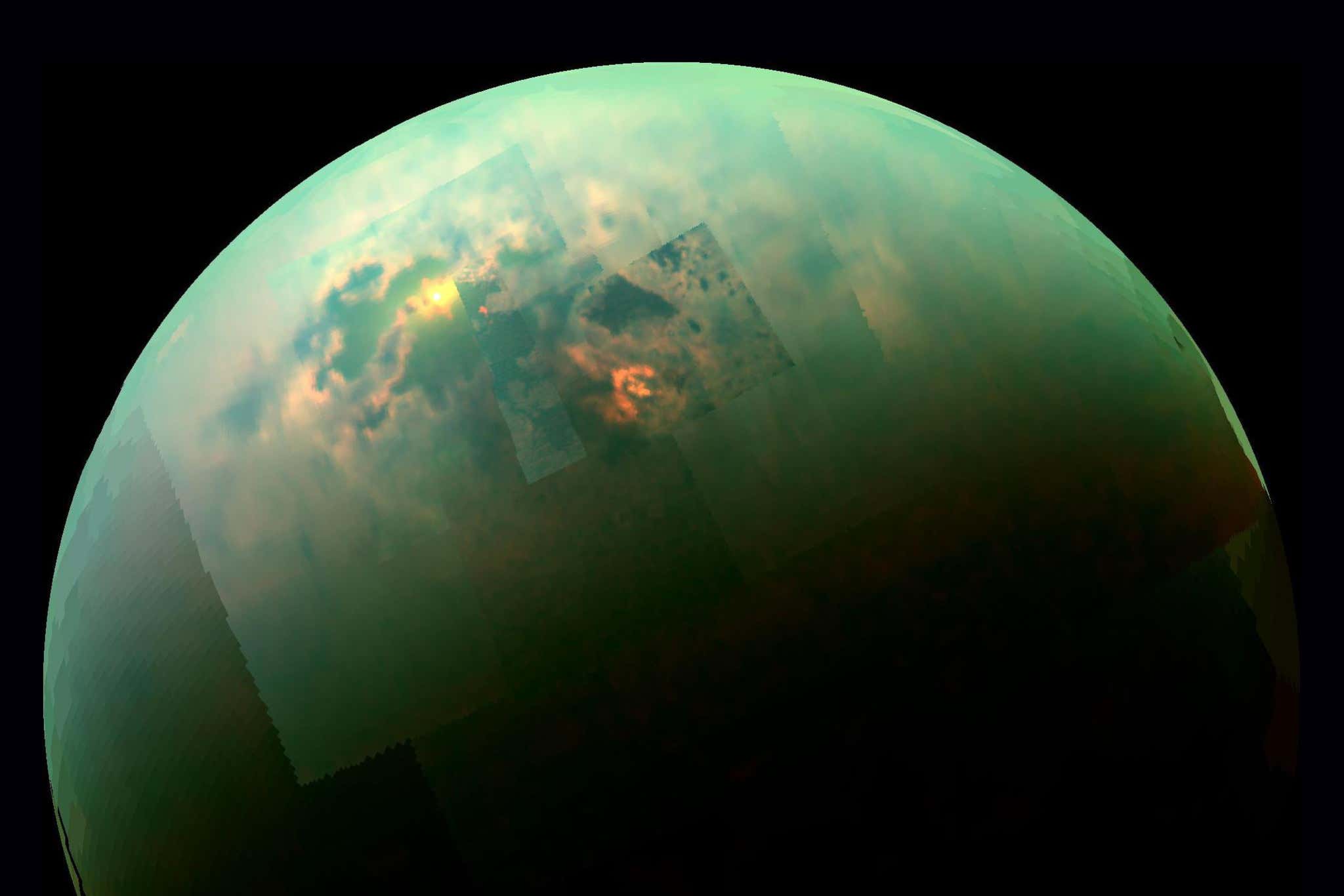

In this paper we present a methodology for automating theclassification of spectrally resolved observations of multiple emissionlines with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).Molecules in planetary atmospheres emit or absorb different wavelengthsof light thereby providing a unique signature for each species. ALMAdata were taken from interferometric observations of Titan made be-tween UT 2012 July 03 23:22:14 and 2012 July 04 01:06:18 as part ofALMA project 2011.0.00319.S. We first employed a greedy set cover algorithm to identify the most probable molecules that would reproducethe set of frequencies with respective flux greater than 3σaway from themean. We then selected a subset of those molecules as present in theatmosphere by specifying a selection threshold and one of two selectionmetrics. Our model was able to correctly classify 100% of previously dis-covered molecules in Titan’s atmosphere from this data, including EthylCyanide as reported by Cardiner et al. (2015)[2]. One molecule, Formalde-hyde, was identified in both selection metrics that was not previouslyrecorded in the atmosphere. The results of our methodology allow for astreamlined approach for molecule classification and anomaly detectionin planetary atmospheres.
S Cocke, A Wilkins, J McDaniel, J Santerre, C Nixon
Full List
Using Machine Learning for Antimicrobial Resistant DNA Identification
JI Lingle, J Santerre
sEMG Gesture Recognition with a Simple Model of Attention
D Josephs, C Drake, A Heroy, J Santerre -
Forecasting Power Consumption in Pennsylvania During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A SARIMAX Model with External COVID-19 and Unemployment Variables
J Au, J Saldaña Jr, B Spanswick, J Santerre
Compressed DNA Representation for Efficient AMR Classification
J Partee, R Hazell, A Solsi, J Santerre
Stationary Exercise Classification using IMUs and Deep Learning
Andrew M Heroy, Zackary Gill, Samantha Sprague, J Santerre
Automated Spectroscopic Detection And Mapping Using ALMA and Machine LearningTechniques
S Cocke, A Wilkins, J McDaniel, J Santerre, C Nixon
Predicting Premature Birth Risk with cfRNA
J Lin, J Marin, J Santerre
Automated Pleural Effusion Detection on Chest X-Rays
N Wall, M Palanisamy, J Santerre